By Dave Mengel, Soil Fertility Specialist
With delayed soybean planting in many areas of the state again this year, many fields look a little rough and variable. One of the questions commonly asked is whether this is due to a nutrient problem. An excellent tool that can be used to answer this question is plant analysis or tissue testing.
As with corn, wheat and other crops, there are two primary ways plant analysis can be used: as a routine monitoring tool to ensure nutrient levels are adequate in the plant in normal or good looking crops, and as a diagnostic tool to help explain some of the variability and problems we see in soybean growth and appearance in fields.
Plant Analysis as a Routine Monitoring Tool
For monitoring nutrient levels purposes, collect 20-30 sets of the upper, fully developed trifoliate leaves, less the petiole, at random from the field anytime between flowering and initial pod set (growth stages R1-4). The top fully developed leaves are generally the dark green leaves visible at the top of the canopy, which are attached at the second or third node down from the top of the stem.
Sampling later, once seed development begins, will give lower nutrient contents since the soybean plant begins to translocate nutrients from the leaves to the developing seed very quickly. Sampling leaf tissue under severe stress conditions for monitoring purposes can also give misleading results and is not recommended.
The sampled leaves should be allowed to wilt overnight to remove excess moisture, placed in a paper bag or mailing envelope, and shipped to a lab for analysis. Growers should not place the leaves in a plastic bag or other tightly sealed container, as they will begin to rot and decompose during transport, and the sample won't be usable.
For what nutrients should you request analysis? In Kansas nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), sulfur, zinc and iron are the nutrients most likely to be deficient in soybeans. Normally the best values are the “bundles” or “packages” of tests offered through many of the labs. The packages can be as simple as N, P and K, or can consist of all of the 14 mineral elements considered essential to plants. Kansas State offers a package that includes N, P, K, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, iron, copper, zinc and manganese for $23.75.
The data returned from the lab will be reported as the concentration of nutrient elements, or potentially toxic elements in the plants. Units reported will normally be in terms of “percent” for the primary and secondary nutrients (N, P, K, calcium, magnesium and sulfur) and “ppm,” or parts per million, for the micronutrients (zinc, copper, iron, manganese, boron, molybdenum and aluminum). Most labs/agronomists compare plant nutrient concentrations to published sufficiency ranges. A sufficiency range is simply the range of concentrations normally found in healthy, productive plants during surveys. A diagram explaining this concept is shown in Figure 1.
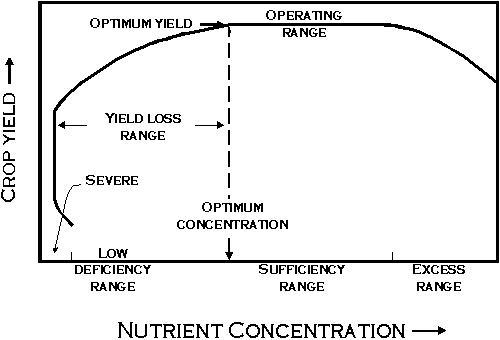 Figure 1. Example of plant analysis interpretation using the concept of a sufficiency range.
Figure 1. Example of plant analysis interpretation using the concept of a sufficiency range.
The following table gives the range of nutrient content considered to be "normal" or "sufficient" for top fully developed soybean leaves at early pod set. Keep in mind that these are the ranges normally found in healthy, productive soybeans.
| Nutrient | Top, Fully Developed Leaves at Pod Set |
| Nitrogen | 4.25-5.5% |
| Phosphorus | 0.25-0.5% |
| Potassium | 1.7-2.5% |
| Calcium | 0.35-2.00% |
| Magnesium | 0.26-1.00% |
| Sulfur | 0.15-0.50% |
| Copper | 10-30 ppm |
| Iron | 50-350 ppm |
| Manganese | 20-100 ppm |
| Zinc | 20-50 ppm |
| Boron | 20-55 ppm |
| Molybdenum | 1-5 ppm |
| Aluminum | <200 ppm |
Plant Analysis as a Diagnostic Tool
Plant analysis is an excellent diagnostic tool to help understand some of the variation seen in the field. When using plant analysis to diagnose field problems, producers should try to take comparison samples from both good/normal areas of the field and problem areas. Collect soil samples from the same good and bad areas, and don’t wait for flowering to sample soybeans.
Early in the season, when plants are 8-10 inches tall, collect whole plants from 15-20 different places in the sampling areas. Later in the season, collect 20-30 sets of top, fully developed leaves. Handle the samples the same as those for monitoring, allowing them to wilt to remove excess moisture and avoiding mailing in plastic bags.
Soil samples are important in diagnostic work, because while a plant may be deficient in a nutrient, it may not be due to a shortage in the soil. Other factors such as soil compaction, insect or disease damage to the roots, low pH limiting nodulation or many other issues can limit nutrient uptake in soybeans.
Summary
In summary, plant analysis is a good tool growers can use to monitor the sufficiency of soil fertility levels and inoculant effectiveness, and a very effective diagnostic tool. Growers should consider adding this to their toolbox.






Post a comment
Report Abusive Comment