With increasing use of cover crops for different goals, we receive more questions each year regarding potential impacts of different herbicide programs on cover crops.
When it comes to herbicides, keep in mind that herbicides have been tested for safety on the crops they are labeled for and often cover crops are not listed as a labeled crop. Thus, working with cover crops requires thinking outside the box on how to use herbicides effectively. One also needs to respect what the herbicide is labeled to do: kill weeds for foliar active herbicides and/or prevent weed seeds from emerging when applying residual herbicides. Thus, it’s important not to attempt seeding cover crops in situations where they aren’t going to succeed due to an herbicide with longer residual activity or an herbicide that may injure a specific cover crop species being considered.
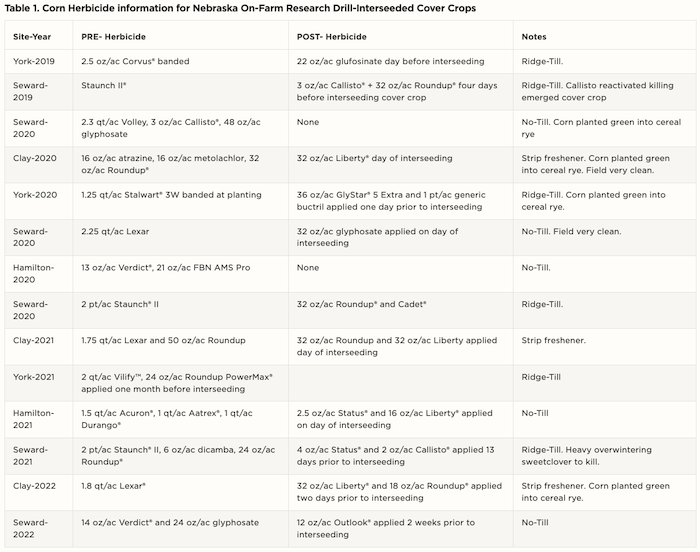
The following are the herbicide programs we have used when interseeding cover crops into corn and soybean early in the growing season. This effort was a partnership amongst The Nature Conservancy, Upper Big Blue NRD, Nebraska Extension, Kelloggs, and cooperating farmers. We successfully achieved germination and establishment of a variety of interseeded cover crops (grasses, legumes, brassicas) in the 2019-2022 growing seasons in Nebraska.
Corn Herbicide Program for Drill Interseeding into V3-V4 Corn
1. We have utilized PRE- herbicides at the recommended label rate. PRE’s included a variety of products (Table 1).
2. By the time the corn was V3-V4, the PRE herbicide residual was no longer impacting the seeding zone (1/4-inch to one inch) for the interseeded cover crops.
3. Often the day before, day of, or day after interseeding cover crops, producers applied: glyphosate, dicamba (often Status®), Liberty® or a combination of products with no issues.
a. One grower conducted an herbicide comparison between a full rate of generic Lexar® PRE- vs. split applied. The split application applied half the rate PRE and the other half rate was applied seven days prior to interseeding. In that case, every species still emerged but growth was thin compared to the full rate of product applied PRE-plant. This video shows what he learned.
4. None of the growers chose this option, but for those desiring a residual herbicide, a Group 15 product (ex. Zidua®, Outlook®, Warrant®, Dual®) can be used once the cover crop is at least one inch tall as this herbicide mode of action has little to no postemergence activity.
Soybean Herbicide Program for Drill Interseeding into VC Soyben
Of note on this study, we used winter wheat as a cover crop species. Had it survived the growing season into the fall, that can be problematic creating a “green bridge” for the wheat curl mite in areas where wheat is often planted. In our studies, the winter wheat died during July, but if one wishes to err on the side of caution, a different grass species can be interseeded (or just interseed red/white clover) in areas where higher acres of wheat are planted.

1. Soybean PRE- emergence herbicide was only used if it was applied at least three weeks before interseeding the cover crop (Table 2). Otherwise, only a burndown of glyphosate and/or dicamba could be used before planting soybean.
2. Cover crop of wheat and red clover was interseeded into VC or V2 soybean. Warm conditions allowed the wheat to emerge within three days. In both fields, no POST herbicide was used.
3. Neither grower chose this option, but for those desiring a residual herbicide, a Group 15 product (ex. Zidua®, Outlook®, Warrant®, Dual®) can be used once the cover crop is at least one inch tall as this herbicide mode of action has little to no postemergence activity.
Table 2. Soybean Herbicide Information for Nebraska On-Farm Research Drill-Interseeded Cover Crops
| Site-Year | Burndown and PRE- | POST- | Notes |
| Seward-2021 | 6 oz/ac Zidua, 24 oz/ac glyphosate, 1 pt/ac Lo-Vol 6 2,4-D applied four weeks before interseeding | None | No-Till. Cereal rye terminated prior to soybean planting |
| Clay-2021 | 32 oz/ac Roundup, Valor, and Zidua PRO applied 4.5 weeks prior to interseeding | None | No-Till. Cereal rye terminated day of planting soybean. |
Soybean Study with Wheat Planting Timing for Weed Control
A study was conducted at UNL’s South Central Ag Lab where wheat was planted on April 4 and then soybean was planted a month later on May 4. Prefix® (Dual II Magnum® + Fomesafen) was applied at 2.5 pint/acre + Metribuzin 75DF at 6 oz/acre after planting soybean when wheat was green and actively growing. No injury on wheat was observed (Figure 2).

The same study had wheat seeded at the same time of soybean planting on May 4. Sharpen® was applied PRE at 1 fl oz/ac after wheat and soybean planting on the same day. No injury on wheat or soybean was noticed and a combination of Sharpen® and wheat provided excellent control of waterhemp and Palmer amaranth (Figure 3). The photo was taken two weeks after applying Sharpen®.
Interseeding Late in the Season at Corn and Soybean Senescence
Because residual herbicides would have broken down other than for extremely dry conditions, we don’t have additional herbicide considerations for broadcast interseeding cover crops during corn and soybean senescence. The Guide for Weed, Disease and Insect Management also shares Replant Options and Rotation Restrictions for some cover crop species and is a resource in addition to the herbicide label.
Overwintering Cover Crop Survival and Herbicides
Some cover crop species are planted the previous year with the goal of them overwintering to the next spring. Reasons for this can include providing weed and/or soil erosion control, grazing and nitrogen.
Some growers have desired for specific cover crop species to survive herbicide applications, while other growers have asked what specific herbicides will kill specific cover crop species.
For example, some growers who planted cereal rye and hairy vetch together wanted to know how to terminate the rye without terminating the vetch. The goal was to allow the vetch to gain more biomass and produce more nitrogen for the corn crop. The farmers we cooperated with found the cereal rye can be terminated using glyphosate at 22-24 fl oz/ac, which we’ve found doesn’t kill the hairy vetch. The hairy vetch can then be terminated with a POST- herbicide application containing an HPPD inhibitor (Group 27 herbicide such as Callisto®, Laudis®, Impact®/Armezon®).
| Herbicide Timing and Product | Overwintering Cover Crop Species Reaction Observed Spring 2021 and Spring 2022 |
| PRE-Lexar (& generic), Callisto | Sweetclover, few red clover, few hairy vetch survived. Nodules quit fixing for 30 days, then resumed fixing (were pink). |
| PRE-Acuron | Sweetclover survived. Most red clover and vetch died. Nodules quit fixing for 30 days then resumed fixing (were pink). |
| PRE- & Burndown Glyphosate | Grasses eventually died. Hairy vetch, clover, sweetclover, collards survived. |
| PRE- & Burndown 2,4-D | Sweetclover, hairy vetch, some collards survived. |
| PRE- & Burndown Dicamba | Sweetclover survived. Some hairy vetch and red clover survived. |
| POST- Glyphosate | Grasses died. Killed volunteer cover crop seedlings. |
| POST- Callisto | Some sweetclover survived. Killed vetch, red clover, collards. |
| POST- Liberty | Burned some sweetclover but much survived. |
| POST- Liberty + Status | Killed most of the sweetclover. |
| POST- Status + Callisto | Killed most of the sweetclover. Cultivation killed the rest. |
Figure 4 was developed based on Jenny Rees’ observations of herbicide interactions with overwintering cover crops that were interseeded in June of the previous growing season. This is based on the springs of 2021 and 2022 with fields located in Clay, Hamilton, York and Seward counties in silt-loam or silty clay-loam soils. These observations may not hold true for other field locations and/or other soil textures. These are observations and no specific research of specific herbicides on specific cover crops was done to formulate Figure 4.
Summary
Many herbicide labels do not contain specific information for cover crops, yet it is important to consult the herbicide label to doublecheck.
It’s also important to view the labels for any grazing restrictions. A quick reference can be found in the Forage, Feed and Grazing Restrictions for Row Crop Herbicides regarding the herbicides applied to the corn and soybean crop when a cover crop is also growing.
Using cover crops in corn and soybean cropping systems takes more management and considering herbicide options is important.
The suggestions contained in this article are based on what we’ve tried via on-farm research in farmers’ fields and not based on specific herbicide-related research. Results may vary based on location.






Post a comment
Report Abusive Comment